

Specifying the direction of deviation of the distal fragment is the most consistent way to describe the direction. Angulated – Degrees and direction to convey the amount of “unbending” needed to realign the fragments.Segmental – There are multiple fractures in one bone that create one or more separate pieces in the middle, or “segments.”.Displaced – A displaced fracture is a broken bone that snaps so far out of place that the two ends no longer line up straight.Nondisplaced – The fractured bone does not move out of place (a clean break).

It is most common after severe trauma, such as a car accident, and is more likely to occur in the hands or feet
COMPLETE BONE FRACTURE SKIN
COMPLETE BONE FRACTURE CRACK
Incomplete or Partial Fracture – There is a crack that does not reach across the entire width of the bone.It is snapped or crushed into two or more pieces. Complete Fracture – In a complete fracture, your bone breaks completely.These are the main types of fractures in terms of how severe they are: The severity of the fracture affects the level of pain you experience. One thing most fractures have in common is the pain they cause. Displaced and non-displaced fractures refer to the alignment of the fractured bone. There are many types of fractures, but the main categories are displaced, non-displaced, open, and closed. As you age, your bones naturally become more brittle making you more likely to suffer fractures that probably would not have occurred in youth. Broken bones are very common in childhood, although children’s fractures are generally less complicated than fractures in adults. Your risk of fracture depends on many factors, but age is the biggest factor. They occur when the physical force exerted on the bone is stronger than the bone itself. The average person experiences two fractures during a lifetime.
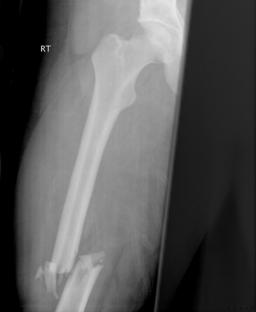
A fracture is the medical term for a broken bone and is a common injury. They allow us the ability to interact with our environment and lift out body up against gravity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
